git笔记记录。

git 是目前全世界最流行的分布式版本控制工具,与之前的集中化的版本控制系统相比,它有如下的优势
- 项目管理更安全。集中式版本控制系统,只要服务器崩溃,那所有人的代码都将丢失。git 的每个项目参与者都会在自己的本地保存一份完整的代码备份,即便其中的一个或者多个电脑出现问题,依然可以通过其他人的代码恢复。
- 不需要联网也可以管理。git 在本地有一套自己完整的版本管理机制,即便断网程序员也可以在本地进行修改,添加或者删除文件,将自己的代码提交到本地的版本库,所有的操作都被忠实得记录在本地版本库中,到时候只要联网恢复,将本地的所有修改 push 到远端的服务器即可。
核心概念
git 的版本管理基于如下的概念框架,只有掌握这些概念才能理解它指令之后的真正含义。核心的 git 框架如下图所示
我们先不用管其中的横向的命令,仅仅关注其中的 4 个圆柱体,分别代表不同的实体,本地包括 workspace, index 和 local repository 三个部分,在服务器端有 remote repository,下面分别详细介绍它们
- workspace, 本地的工作目录,它是 Git 用来保存元数据和对象数据库的地方,添加,修改,删除等操作就在这个目录里面进行;
- index, 暂存区域,这是 git 的缓存机制,在 workspace 的修改可以暂存在这个区域;
- local repository,本地仓库,我们将 index 区域的代码提交到本地仓库,就完成一次完整的修改。
- remote repository,远端仓库,这是远端服务器存放代码的地方,比如现在非常流行的 GitHub,可以将本地仓库的代码推送到远端仓库,供其他人浏览和下载。
文件状态
workspace 里面的文件无外乎两种状态:已跟踪或者未跟踪。如果文件已经被纳入到版本管理中就为已跟踪,直观的理解就是之前在版本库里添加或者提交过该文件,版本库有该文件的记录,它已经感知到该文件的存在;如果该文件从未提交或者添加到版本库中,那么它就是未被跟踪的。
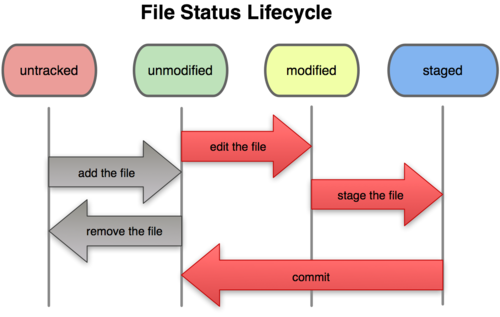
如下图所示,比如你在 workspace 里面新建了一个文件,之后没有任何动作,此时该文件是未跟踪状态,但是如果你将它添加到暂存区域,或者之后又提交到本地仓库,那么就变成了已跟踪状态。
基本流程
下面我们结合具体的实例,介绍下使用 git 在本地进行版本管理的流程,重点是熟悉基本的操作以及其中所用到的指令。我最近在学习 C++,需要根据《C++ primer plus》写一些小程序进行练习,及时记录学习的进度,所以我自己在本地新建一个 git 仓库管理这些文件。
创建 git 仓库
|
|
这是使用 git 的基础,我们有两种方式创建仓库
-
本地新建。我在本地创建文件夹 C++ primer plus,然后在 windows 下切换到该目录下,使用敲入
git init,命令行提示1 2$ git init Initialized empty Git repository in D:/Study/C++ primer plus/.git/
初始化后,在当前目录下会出现一个名为.git的目录,所有 Git 需要的数据和资源都存放在这个目录中。,自己不要去修改它。
- 远端下载。我可如果想对某个开源项目出一份力,可以先把该项目的 Git 仓库复制一份出来,这就需要用到
git clone命令。比如我想将 ss-qt5 的代码拉下来,可以使用如下的指令git clone git@github.com:shadowsocks/shadowsocks-qt5.git,拉下来的基本格式是git clone [url],之后在我的本地电脑就有一份完整的该项目的代码
检查文件状态
|
|
在添加文件之前,先介绍一个非常有用的命令git status,它可以查看当前版本库中的所有文件状态,包括已跟踪或者未跟踪的文件。
git status会将 workspace 和暂存区的文件比对,同时比对本地仓库有暂存区的文件。
在当前的目录下,敲入该命令,输出如下
|
|
这个提示说明,现在的工作目录相当干净,所以已经跟踪的文件在上次提交之后没有被修改过。而且,在当前的目录中没有任何还没有被跟踪的新文件,当前工作的分支是master,凡事本地创建分支默认都是这个名字,后续分支管理可以改变分支,下篇再介绍。
添加文件
|
|
创建本地仓库之后,就可以在仓库里面添加文件了。我在仓库里面新建readme.txt文件,并在文件中写入
|
|
使用git status查看当前的窗台状态,显示如下
|
|
显示可能会有差异,我将其中的空行去掉了,这段话表明当前文件readme.txt还没有被跟踪 (untracked),当前没有文件需要添加,使用git add <file>将其跟踪。那我们使用git add readme.txt跟踪该文件,命令行没有任何回应,表明一切正常。之后再次使用git status查看如下
|
|
显示当前的readme.txt已经进入暂存区,该文件可以被 committed。
**git add 的潜台词就是把目标文件快照放入暂存区域,也就是 add file into staged area,同时未曾跟踪过的文件标记为需要跟踪。**如果一次需要添加所有的文件,可以使用
git add .,其中的.表示当前工作区中的所有文件。
我继续修改readme.txt文件,添加一行this is the 2nd line,之后再添加文件test.cc,查看文件状态,显示如下
|
|
这里有比较有意思的地方,test.cc与之前的readme.txt一样,后来新加的文件,因此它显示该文件未被跟踪。这里需要详细说明一下readme.txt,现在在 workspace 和 index 的暂存区都有该文件,但是两个文件的内容不同,workspace 中的是最新的修改版本,包含了第 2 行,但是 index 中的仅仅包含第一行(因为第 2 次修改之后还没有git add),所以才会有两条显示信息。
-
暂存区与本地版本库相比,还有些修改 (第 1 行) 没有 commit;
-
workspace 与暂存区相比,还有些修改 (第 2 行) 没有被跟踪。
所以,可以看出 git 记录的是文件的修改而不是文件本身。现在使用
git add readme.txt则将会把 workspace 中的新修改一并跟踪并记录在暂存区中,如下所示
|
|
此时的readme.txt已经是 to be committed 状态了,之前的 workspace 中的修改已经被跟踪了。
提交修改
提交修改就是将暂存区的文件以及它们的修改提交到本地仓库,使用git commit -m "balabla",该命令将所有的暂存区中的文件提交到本地仓库,双引号中的字符是提交的说明,输入该命令将readme.txt提交到本地仓库,如下所示
|
|
表示暂存区的所有文件已经提交,此时查看状态如下
|
|
说明工作区很干净,workspace/index/local repository 三个区的所有东西都是一致的没有任何的差异。
查看提交历史
|
|
在下一节之前,先学会查看本地的提交历史,使用git log可以查看本仓库的从最近到最远的所有提交历史,如下图所示【图片暂缺】
|
|
可以看出一共有 3 次提交,每个提交中包含自己的 commit_id,作者以及提交的具体时间。commit 之后的那一长串字母和数字,唯一标记每次 git 的提交,类似于 SVN 中的提交 id,之所以用这么一长串的十六进制的数字表示是为了避免很多人在同一版本库中提交时候发生冲突。如果提交的次数很多,这么看就比较长了,可以使用git log --pretty=oneline来查看比较简略的版本,如下所示
|
|
仅仅包含每次提交的 id 以及说明,看起来一目了然。此外还可以使用gitk使用图形化界面查看提交历史,如下图所示

撤销修改
|
|
如果发现代码修改有问题,就需要撤销修改,这里依照不同的存储位置,分为如下三种情况。
撤销 workspace 中的修改
我在readme.txt文件中不小心添加了一行字,文件内容如下
|
|
幸好及时发现,我们现在要做的就是将最后一行去掉,依然使用git status查看工作区的文件,可以看到如下的结果
|
|
明显可以看出文件的修改还没有被跟踪,而且提示我们使用git checkout -- <file>来放弃对工作区文件的修改,那我们试试看输入git checkout -- readme.txt,使用该命令后果然最后一行不见了。
撤销暂存区中的修改
依然以上面的文件为例,我在文件末尾添加那一句my boss is an idiot,之后使用git add readme.txt添加到暂存库,查看状态
|
|
提示我可以使用git reset HEAD <file>放弃修改,使用该命令看看
|
|
可以看出修改又回复到之前在工作区的状态,继续使用git checkout -- readme.txt彻底撤销之前的修改。
撤销本地仓库中的修改
之前的撤销相对比较容易,如果已经提交到了本地仓库该撤销修改呢?现在我们修改readme.txt文件为如下内容
|
|
然后git add .,git commit -m "hahahaha",这样就提交到了本地仓库,查看提交历史,如下所示
|
|
代码已经提交了。可以使用git reset --hard HEAD^放弃这次修改。这条指令的解析如下
git reset,表示回退,这个指令既可以将暂存区的数据回退到工作区,也可以回退版本。--hard,表示回退版本的同时,将工作区和暂存区的文件内容也同步回退,这里还有两个选项,具体见下表
| 参数 | 意义 |
|---|---|
hard |
仅仅回退版本,修改工作区和暂存区文件 |
mixed |
回退版本,修改暂存区文件,不修改工作区 |
merge |
回退版本,修改暂存区文件,修改工作区中那些被跟踪的文件 |
soft |
仅仅回退版本,不修改工作区和暂存区文件 |
HEAD表示当前版本的指针所在,HAED^表示前一个版本,HEAD^^表示之前两个版本,如果是前 100 个版本则可以使用HEAD~100。
使用该命令之后的结果如下
|
|
此外,也可以直接指定版本号,回退到特定的版本,比如我想回退到最早的那个版本,可以使用如下的命令git reset --hard abbd1c,后面的版本号就是第一次提交的 commit_id 的前几位,不必全部都写全,系统可以区分其他版本即可。输出结果如下
|
|
现在已经回退到之前最早的版本了。
误删怎么办
如果误删,可以使用git reflog,它记录了我们所有的操作,可以看到之前的 commit_id 以及对应的说明,如下所示
|
|
如果要恢复到hahahaha的版本,可以使用如下的指令
|
|
修改成功~
所有上面的操作可以总结在如下的一张图里
参考资料
- Git Tutorial - Try Git
- Git 与 Repo 简单入门 - 简书
- Pro Git 简体中文版,非常全面的 git 小书
- Git 教程 - 廖雪峰的官方网站,有对应的 ios 的 Git App for iOS - 廖雪峰的官方网站
- 图解 Git